Design Thinking is a human-centered, empirical research method that employs user-centric methods (e.g., customer discovery interviews, focus groups, usability studies) to solve problems and develop products and applications that people want.
People (e.g., founders, product managers, developers, engineers) engage in design thinking when they set aside their egos and endeavor to listen to consumers and stakeholders in a probleplans and conduct customer discovery interviews; focus groups, usability studies.
Design Thinking may also be referred to as Venture Design.
Key Concepts: Customer Discovery; Design; Design Thinking; Lean Product Development; Mixed Research Methods; Problem Definition; Problem Space; Rhetoric; Venture Design.
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is an epistemology, an ideology, a way of developing knowledge claims. Design Thinking presumes people (e.g., founders, product managers, developers, engineers) should build not what they believe a customer needs but rather what the customer tells them they need.
Design Thinking is a research method that focuses on the customer. Design Thinking may occur as a formal research method. When investigators aim to interview subjects for research that will be disseminated to a broad audience then that research needs to be approved and monitored by IRB. However, Design Thinking is often engaged in as form of informal research.
Design Thinking is a method used to investigate the feasibility, desirability, and viability of a business idea.
Design Thinking relies on dialectic, hermeneutics.
Design Thinking is an interdisciplinary field of study. Design Thinking is a topic of research and theory across disciplines, including Art, Information Studies, Engineering, Writing Studies.
Design Thinking is a rhetorical process. Design Thinking shares rhetoric’s focus on the user: In order for a text to be lucid, the writer must focus on audience. For a product or service to be viable, it must solve the needs of its customers.
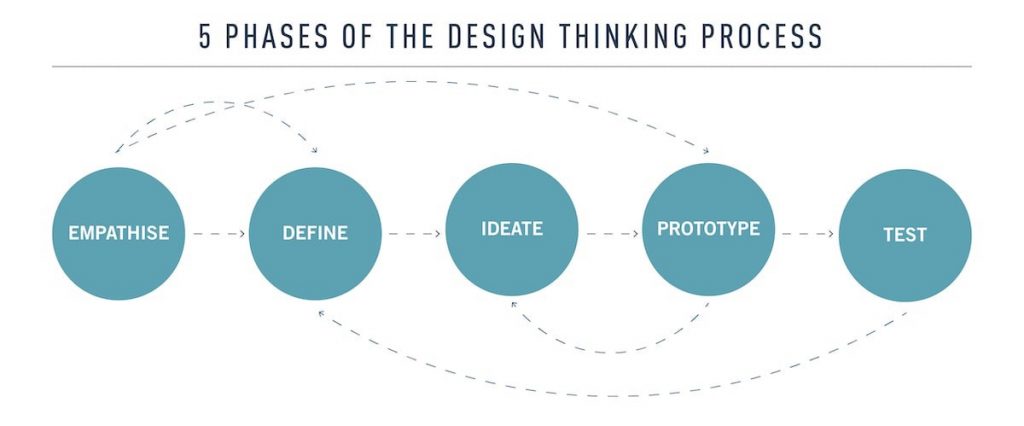
Stages of Design Thinking
In the product-development literature, Design Thinking is attributed to having five, interrelated, recursive stages:
- Empathise
- Define
- Ideate
- Prototype
- Test
- Empathise
- How does the customer experience of the problem? What customer personas can you identify?
- Define
- What does the customer need? What are the pain points experienced by the customer?
- what have you customer-discovery interviewes told youDevelop your Problem Statement
- Ideate
- Brainstorming–etc.
- Prototype
- Minimum Viable Product
- Test
Recommended Readings
Stevens, E. (2023, January 4). What Is design thinking? A comprehensive beginner’s guide. Career Foundry. https://careerfoundry.com/en/blog/ux-design/what-is-design-thinking-everything-you-need-to-know-to-get-started/
Dam, R. F., & Siang. T. Y. (2022, July). What is design thinking and why is it so popular? Interaction Design Foundation. https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/what-is-design-thinking-and-why-is-it-so-popular